Vamos a ver como a configurar Jupyter Notebook en un maquina con Ubuntu 18.04, y aprender a conectarse al Notebook y a utilizarlo. Jupyter Notebooks (o simplemente Notebooks) es un conjunto de documentos producidos por la aplicación Jupyter Notebook, la cual contiene tanto elementos de código icomo de texto enriquecido (párrafos, ecuaciones, cifras y enlaces, entre otros) que ayudan a presentar y compartir la investigación que puede reproducirse.
Al final de esta guía, podrá ejecutar código de Python 3 usando un Jupyter Notebook en ejecución.
Para iniciar el proceso, instalaremos las dependencias que necesitamos para nuestro entorno de programación de Python desde los repositorios de Ubuntu. Ubuntu 18.04 viene con Python 3.6 previamente instalado. Usaremos el administrador de paquetes de Python pip para instalar componentes adicionales más tarde.
Necesitaremos primero actualizar el índice de paquetes local apt y luego descargaremos e instalaremos los paquetes:
sudo apt update A continuación, instale pip y los archivos de encabezado de Python, utilizados por algunas dependencias de Jupyter:
sudo apt install python3-pip python3-dev Ahora podemos proceder a configurar un entorno virtual de Python en el que instalaremos Jupyter.
Crear un entorno virtual de Python para Jupyter
Ahora Python 3, sus archivos de encabezado y pip están listos para comenzar, podemos crear un entorno virtual de Python para administrar nuestros proyectos. Instalaremos Jupyter en este entorno virtual.
Para ello, primero necesitaremos acceso al comando virtualenv, que podemos instalar con pip.
Actualice pip e instale el paquete escribiendo lo siguiente:
sudo -H pip3 install --upgrade pip sudo -H pip3 install virtualenv El indicador -H garantiza que la política de seguridad defina la variable de entorno home como el directorio de inicio del usuario de destino.
Con virtualenv ya instalado, podemos comenzar a crear nuestro entorno. Cree un directorio en el que podamos guardar los archivos de nuestro proyecto y posiciónese en él: Daremos a este directorio el nombre my_project_dir, pero deberá usar un nombre que sea significativo para usted y para el trabajo que está desarrolle.
mkdir ~/my_project_dir cd ~/my_project_dir En el directorio del proyecto, crearemos un entorno virtual de Python. A los efectos de este tutorial, le daremos el nombre my_project_env, pero debería asignarle uno que se relacione con su proyecto.
virtualenv my_project_env Con esto, se creará un directorio llamado my_project_env dentro de su directorio my_project_dir. Dentro de este, se instalarán una versión local de Python y una versión local de pip. Podemos usar esto para instalar y configurar un entorno aislado de Python para Jupyter.
Antes de instalar Jupyter, debemos activar el entorno virtual. Puede hacerlo escribiendo lo siguiente:
source my_project_env/bin/activate
Su línea de comandos cambiará para indicar que ahora realizará operaciones en un entorno virtual de Python. Tendrá un aspecto similar al siguiente: (my_project_env)[email protected]:~/my_project_dir$.
Con esto, estará listo para instalar Jupyter en este entorno virtual.
Instalar Jupyter
Una vez activado su entorno virtual, instale Jupyter con la instancia local de pip.
Nota: Cuando se active el entorno virtual (cuando (my_project_env) se encuentre al inicio de su línea de comandos), use pip en lugar de pip3, incluso si emplea Python 3. La copia del entorno virtual de la herramienta siempre se llama pip, independientemente de la versión de Python.
pip install jupyter En este punto, habrá instalado con éxito todo el software necesario para ejecutar Jupyter. Ahora podremos iniciar el servidor de Notebook.
Ejecutar Jupyter Notebook
Ya dispone de todo lo que necesita para ejecutar Jupyter Notebook. Para ejecutarlo, introduzca el siguiente comando:
jupyter notebook Se mostrará un registro de las actividades de Jupyter Notebook en el terminal. Cuando se ejecuta Jupyter Notebook, este funciona en un número de puerto específico. Normalmente, el primer notebook que ejecute usará el puerto 8888. Para verificar el número de puerto específico en el que se ejecuta Jupyter Notebook, consulte el resultado del comando utilizado para iniciarlo:
Output[I 21:23:21.198 NotebookApp] Writing notebook server cookie secret to /run/user/1001/jupyter/notebook_cookie_secret
[I 21:23:21.361 NotebookApp] Serving notebooks from local directory: /home/sammy/my_project_dir
[I 21:23:21.361 NotebookApp] The Jupyter Notebook is running at:
[I 21:23:21.361 NotebookApp] http://localhost:8888/?token=1fefa6ab49a498a3f37c959404f7baf16b9a2eda3eaa6d72
[I 21:23:21.361 NotebookApp] Use Control-C to stop this server and shut down all kernels (twice to skip confirmation).
[W 21:23:21.361 NotebookApp] No web browser found: could not locate runnable browser.
[C 21:23:21.361 NotebookApp]
Copy/paste this URL into your browser when you connect for the first time,
to login with a token:
http://localhost:8888/?token=1fefa6ab49a498a3f37c959404f7baf16b9a2eda3eaa6d72
Si ejecuta Jupyter Notebook en una computadora local (no en un servidor), puede dirigirse a la URL que se muestra para conectarse a Jupyter Notebook. Si ejecuta Jupyter Notebook en un servidor, deberá establecer conexión con este usando túneles SSH.
Usar Jupyter Notebook
Si Jupyter Notebook aún no está en ejecución, inícielo con el comando jupyter notebook.
Con esto, debería establecer conexión con este usando un navegador web. Jupyter Notebook es una herramienta muy poderosa que dispone de muchas características. En esta sección se mostrarán algunas de las características básicas para que comience a usar el Notebook. Jupyter Notebook mostrará todos los archivos y las carpetas en el directorio desde el que se ejecuta. Por ello, cuando trabaje en un proyecto asegúrese de iniciarlo desde el directorio del proyecto.
Para crear un nuevo archivo de Notebook, seleccione New > Python 3 en el menú desplegable que se encuentra en la parte superior derecha:
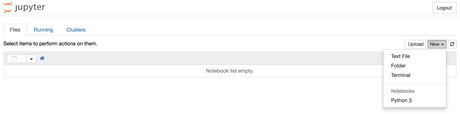
Con esto se abrirá un Notebook. Ahora podemos ejecutar el código de Python en la celda o cambiar la celda a lenguaje de marcado. Por ejemplo, cambie la primera celda para aceptar el lenguaje de marcado haciendo clic en Cell > Cell Type > Markdown en la barra de navegación de la parte superior. Con esto, podremos escribir notas usando el lenguaje de marcado e incluso incluir ecuaciones escritas en LaTeX disponiéndolas entre los símbolos de $$. Por ejemplo, escriba lo siguiente en la celda después del cambio a lenguaje de marcado:
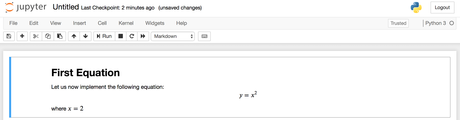
# First Equation Let us now implement the following equation: $$ y = x^2$$ where $x = 2$ Para convertir el lenguaje de marcado en texto enriquecido, presione CTRL + ENTER. Deberían aparecer los siguientes resultados:
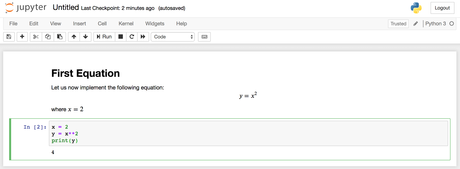
Puede utilizar las celdas de lenguaje de marcado para crear notas y documentar su código. Implementaremos esa ecuación e imprimiremos el resultado. Haga clic en la celda superior y presione ALT+ENTER para añadir una celda debajo de esta. Ingrese el código siguiente en la nueva celda.
x = 2 y = x**2 print(y)Para ejecutar el código, presione CTRL+ENTER. Obtendrá los siguientes resultados:
Ahora podrá importar módulos y usar el Notebook como lo haría con cualquier otro entorno de desarrollo de Python.
A partir de aquí, puede iniciar un proyecto de análisis y visualización de datos o por ejemplo ,si está interesado en abordar el tema en mayor profundidad, puede investigar sobre Visualización y pronóstico de series de tiempo.
Como ejemplo , en las lineas siguientes mostramos una ejecución de los comandos anteriormente vistos:
[email protected]:~$ sudo apt install python3-pip python3-dev [sudo] contraseña para carlos: Leyendo lista de paquetes... Hecho Creando árbol de dependencias Leyendo la información de estado... Hecho python3-dev ya está en su versión más reciente (3.8.2-0ubuntu2). python3-pip ya está en su versión más reciente (20.0.2-5ubuntu1.5). Los paquetes indicados a continuación se instalaron de forma automática y ya no son necesarios. distro-info libfprint-2-tod1 libllvm9 Utilice "sudo apt autoremove" para eliminarlos. 0 actualizados, 0 nuevos se instalarán, 0 para eliminar y 40 no actualizados.[email protected]:~$ sudo -H pip3 install --upgrade pip Requirement already satisfied: pip in /usr/local/lib/python3.8/dist-packages (21.1.3) WARNING: Running pip as the 'root' user can result in broken permissions and conflicting behaviour with the system package manager. It is recommended to use a virtual environment instead: https://pip.pypa.io/warnings/venv[email protected]:~$ sudo -H pip3 install virtualenv Requirement already satisfied: virtualenv in /usr/local/lib/python3.8/dist-packages (20.4.7) Requirement already satisfied: distlib<1,>=0.3.1 in /usr/local/lib/python3.8/dist-packages (from virtualenv) (0.3.2) Requirement already satisfied: six<2,>=1.9.0 in /usr/lib/python3/dist-packages (from virtualenv) (1.14.0) Requirement already satisfied: appdirs<2,>=1.4.3 in /usr/local/lib/python3.8/dist-packages (from virtualenv) (1.4.4) Requirement already satisfied: filelock<4,>=3.0.0 in /usr/local/lib/python3.8/dist-packages (from virtualenv) (3.0.12) WARNING: Running pip as the 'root' user can result in broken permissions and conflicting behaviour with the system package manager. It is recommended to use a virtual environment instead: https://pip.pypa.io/warnings/venv[email protected]:~$ ls Descargas Escritorio Música Público Vídeos Documentos Imágenes Plantillas snap[email protected]:~$ mkdir ~/mi_proyecto_dir[email protected]:~$ mkdir ~/mi_proyecto_dir mkdir: no se puede crear el directorio "/home/carlos/mi_proyecto_dir": El archivo ya existe[email protected]:~$ cd ~/mi_proyecto_dir[email protected]:~/mi_proyecto_dir$ virtualenv mi_proyecto_env created virtual environment CPython3.8.5.final.0-64 in 458ms creator CPython3Posix(dest=/home/carlos/mi_proyecto_dir/mi_proyecto_env, clear=False, no_vcs_ignore=False, global=False) seeder FromAppData(download=False, pip=bundle, setuptools=bundle, wheel=bundle, via=copy, app_data_dir=/home/carlos/.local/share/virtualenv) added seed packages: pip==21.1.2, setuptools==57.0.0, wheel==0.36.2 activators BashActivator,CShellActivator,FishActivator,PowerShellActivator,PythonActivator,XonshActivator[email protected]:~/mi_proyecto_dir$ source mi_proyecto_env/bin/activate (mi_proyecto_env)[email protected]:~/mi_proyecto_dir$ pip install jupyter Collecting jupyter Downloading jupyter-1.0.0-py2.py3-none-any.whl (2.7 kB) Collecting ipykernel Downloading ipykernel-5.5.5-py3-none-any.whl (120 kB) |████████████████████████████████| 120 kB 2.7 MB/s Collecting jupyter-console Downloading jupyter_console-6.4.0-py3-none-any.whl (22 kB) Collecting notebook Downloading notebook-6.4.0-py3-none-any.whl (9.5 MB) |████████████████████████████████| 9.5 MB 9.2 MB/s Collecting qtconsole Downloading qtconsole-5.1.0-py3-none-any.whl (119 kB) |████████████████████████████████| 119 kB 1.6 MB/s Collecting ipywidgets Downloading ipywidgets-7.6.3-py2.py3-none-any.whl (121 kB) |████████████████████████████████| 121 kB 1.6 MB/s Collecting nbconvert Downloading nbconvert-6.1.0-py3-none-any.whl (551 kB) |████████████████████████████████| 551 kB 2.3 MB/s Collecting ipython>=5.0.0 Downloading ipython-7.25.0-py3-none-any.whl (786 kB) |████████████████████████████████| 786 kB 3.2 MB/s Collecting tornado>=4.2 Downloading tornado-6.1-cp38-cp38-manylinux2010_x86_64.whl (427 kB) |████████████████████████████████| 427 kB 3.2 MB/s Collecting traitlets>=4.1.0 Downloading traitlets-5.0.5-py3-none-any.whl (100 kB) |████████████████████████████████| 100 kB 2.9 MB/s Collecting jupyter-client Downloading jupyter_client-6.1.12-py3-none-any.whl (112 kB) |████████████████████████████████| 112 kB 3.3 MB/s Collecting pygments Downloading Pygments-2.9.0-py3-none-any.whl (1.0 MB) |████████████████████████████████| 1.0 MB 4.6 MB/s Requirement already satisfied: setuptools>=18.5 in ./mi_proyecto_env/lib/python3.8/site-packages (from ipython>=5.0.0->ipykernel->jupyter) (57.0.0) Collecting matplotlib-inline Downloading matplotlib_inline-0.1.2-py3-none-any.whl (8.2 kB) Collecting pexpect>4.3 Downloading pexpect-4.8.0-py2.py3-none-any.whl (59 kB) |████████████████████████████████| 59 kB 3.4 MB/s Collecting prompt-toolkit!=3.0.0,!=3.0.1,<3.1.0,>=2.0.0 Downloading prompt_toolkit-3.0.19-py3-none-any.whl (368 kB) |████████████████████████████████| 368 kB 3.5 MB/s Collecting jedi>=0.16 Downloading jedi-0.18.0-py2.py3-none-any.whl (1.4 MB) |████████████████████████████████| 1.4 MB 2.7 MB/s Collecting backcall Downloading backcall-0.2.0-py2.py3-none-any.whl (11 kB) Collecting pickleshare Downloading pickleshare-0.7.5-py2.py3-none-any.whl (6.9 kB) Collecting decorator Downloading decorator-5.0.9-py3-none-any.whl (8.9 kB) Collecting parso<0.9.0,>=0.8.0 Downloading parso-0.8.2-py2.py3-none-any.whl (94 kB) |████████████████████████████████| 94 kB 1.7 MB/s Collecting ptyprocess>=0.5 Downloading ptyprocess-0.7.0-py2.py3-none-any.whl (13 kB) Collecting wcwidth Downloading wcwidth-0.2.5-py2.py3-none-any.whl (30 kB) Collecting ipython-genutils Downloading ipython_genutils-0.2.0-py2.py3-none-any.whl (26 kB) Collecting nbformat>=4.2.0 Downloading nbformat-5.1.3-py3-none-any.whl (178 kB) |████████████████████████████████| 178 kB 3.7 MB/s Collecting widgetsnbextension~=3.5.0 Downloading widgetsnbextension-3.5.1-py2.py3-none-any.whl (2.2 MB) |████████████████████████████████| 2.2 MB 4.5 MB/s Collecting jupyterlab-widgets>=1.0.0 Downloading jupyterlab_widgets-1.0.0-py3-none-any.whl (243 kB) |████████████████████████████████| 243 kB 2.8 MB/s Collecting jsonschema!=2.5.0,>=2.4 Downloading jsonschema-3.2.0-py2.py3-none-any.whl (56 kB) |████████████████████████████████| 56 kB 2.4 MB/s Collecting jupyter-core Downloading jupyter_core-4.7.1-py3-none-any.whl (82 kB) |████████████████████████████████| 82 kB 545 kB/s Collecting six>=1.11.0 Downloading six-1.16.0-py2.py3-none-any.whl (11 kB) Collecting attrs>=17.4.0 Downloading attrs-21.2.0-py2.py3-none-any.whl (53 kB) |████████████████████████████████| 53 kB 1.7 MB/s Collecting pyrsistent>=0.14.0 Downloading pyrsistent-0.17.3.tar.gz (106 kB) |████████████████████████████████| 106 kB 4.7 MB/s Collecting pyzmq>=17 Downloading pyzmq-22.1.0-cp38-cp38-manylinux2010_x86_64.whl (1.1 MB) |████████████████████████████████| 1.1 MB 9.0 MB/s Collecting argon2-cffi Downloading argon2_cffi-20.1.0-cp35-abi3-manylinux1_x86_64.whl (97 kB) |████████████████████████████████| 97 kB 2.4 MB/s Collecting terminado>=0.8.3 Downloading terminado-0.10.1-py3-none-any.whl (14 kB) Collecting Send2Trash>=1.5.0 Downloading Send2Trash-1.7.1-py3-none-any.whl (17 kB) Collecting prometheus-client Downloading prometheus_client-0.11.0-py2.py3-none-any.whl (56 kB) |████████████████████████████████| 56 kB 2.9 MB/s Collecting jinja2 Downloading Jinja2-3.0.1-py3-none-any.whl (133 kB) |████████████████████████████████| 133 kB 5.3 MB/s Collecting python-dateutil>=2.1 Downloading python_dateutil-2.8.1-py2.py3-none-any.whl (227 kB) |████████████████████████████████| 227 kB 6.1 MB/s Collecting cffi>=1.0.0 Downloading cffi-1.14.5-cp38-cp38-manylinux1_x86_64.whl (411 kB) |████████████████████████████████| 411 kB 5.6 MB/s Collecting pycparser Downloading pycparser-2.20-py2.py3-none-any.whl (112 kB) |████████████████████████████████| 112 kB 6.4 MB/s Collecting MarkupSafe>=2.0 Downloading MarkupSafe-2.0.1-cp38-cp38-manylinux2010_x86_64.whl (30 kB) Collecting defusedxml Downloading defusedxml-0.7.1-py2.py3-none-any.whl (25 kB) Collecting jupyterlab-pygments Downloading jupyterlab_pygments-0.1.2-py2.py3-none-any.whl (4.6 kB) Collecting pandocfilters>=1.4.1 Downloading pandocfilters-1.4.3.tar.gz (16 kB) Collecting entrypoints>=0.2.2 Downloading entrypoints-0.3-py2.py3-none-any.whl (11 kB) Collecting testpath Downloading testpath-0.5.0-py3-none-any.whl (84 kB) |████████████████████████████████| 84 kB 2.3 MB/s Collecting nbclient<0.6.0,>=0.5.0 Downloading nbclient-0.5.3-py3-none-any.whl (82 kB) |████████████████████████████████| 82 kB 156 kB/s Collecting mistune<2,>=0.8.1 Downloading mistune-0.8.4-py2.py3-none-any.whl (16 kB) Collecting bleach Downloading bleach-3.3.0-py2.py3-none-any.whl (283 kB) |████████████████████████████████| 283 kB 2.0 MB/s Collecting async-generator Downloading async_generator-1.10-py3-none-any.whl (18 kB) Collecting nest-asyncio Downloading nest_asyncio-1.5.1-py3-none-any.whl (5.0 kB) Collecting webencodings Downloading webencodings-0.5.1-py2.py3-none-any.whl (11 kB) Collecting packaging Downloading packaging-20.9-py2.py3-none-any.whl (40 kB) |████████████████████████████████| 40 kB 2.3 MB/s Collecting pyparsing>=2.0.2 Downloading pyparsing-2.4.7-py2.py3-none-any.whl (67 kB) |████████████████████████████████| 67 kB 2.3 MB/s Collecting qtpy Downloading QtPy-1.9.0-py2.py3-none-any.whl (54 kB) |████████████████████████████████| 54 kB 1.6 MB/s Building wheels for collected packages: pyrsistent, pandocfilters Building wheel for pyrsistent (setup.py) ... done Created wheel for pyrsistent: filename=pyrsistent-0.17.3-cp38-cp38-linux_x86_64.whl size=106707 sha256=e6bbf1c3ab821bff25db37c383511188da3a4f86108ffafb72e36a85a06af1a7 Stored in directory: /home/carlos/.cache/pip/wheels/3d/22/08/7042eb6309c650c7b53615d5df5cc61f1ea9680e7edd3a08d2 Building wheel for pandocfilters (setup.py) ... done Created wheel for pandocfilters: filename=pandocfilters-1.4.3-py3-none-any.whl size=8006 sha256=b9ea03260cb4b2803d7d4ce8b6af9838ccd6c5a1509e73f783636910928a9d84 Stored in directory: /home/carlos/.cache/pip/wheels/fc/39/52/8d6f3cec1cca4ceb44d658427c35711b19d89dbc4914af657f Successfully built pyrsistent pandocfilters Installing collected packages: ipython-genutils, traitlets, six, pyrsistent, attrs, wcwidth, tornado, pyzmq, python-dateutil, pyparsing, ptyprocess, parso, jupyter-core, jsonschema, webencodings, pygments, pycparser, prompt-toolkit, pickleshare, pexpect, packaging, nest-asyncio, nbformat, matplotlib-inline, MarkupSafe, jupyter-client, jedi, decorator, backcall, async-generator, testpath, pandocfilters, nbclient, mistune, jupyterlab-pygments, jinja2, ipython, entrypoints, defusedxml, cffi, bleach, terminado, Send2Trash, prometheus-client, nbconvert, ipykernel, argon2-cffi, notebook, widgetsnbextension, qtpy, jupyterlab-widgets, qtconsole, jupyter-console, ipywidgets, jupyter Successfully installed MarkupSafe-2.0.1 Send2Trash-1.7.1 argon2-cffi-20.1.0 async-generator-1.10 attrs-21.2.0 backcall-0.2.0 bleach-3.3.0 cffi-1.14.5 decorator-5.0.9 defusedxml-0.7.1 entrypoints-0.3 ipykernel-5.5.5 ipython-7.25.0 ipython-genutils-0.2.0 ipywidgets-7.6.3 jedi-0.18.0 jinja2-3.0.1 jsonschema-3.2.0 jupyter-1.0.0 jupyter-client-6.1.12 jupyter-console-6.4.0 jupyter-core-4.7.1 jupyterlab-pygments-0.1.2 jupyterlab-widgets-1.0.0 matplotlib-inline-0.1.2 mistune-0.8.4 nbclient-0.5.3 nbconvert-6.1.0 nbformat-5.1.3 nest-asyncio-1.5.1 notebook-6.4.0 packaging-20.9 pandocfilters-1.4.3 parso-0.8.2 pexpect-4.8.0 pickleshare-0.7.5 prometheus-client-0.11.0 prompt-toolkit-3.0.19 ptyprocess-0.7.0 pycparser-2.20 pygments-2.9.0 pyparsing-2.4.7 pyrsistent-0.17.3 python-dateutil-2.8.1 pyzmq-22.1.0 qtconsole-5.1.0 qtpy-1.9.0 six-1.16.0 terminado-0.10.1 testpath-0.5.0 tornado-6.1 traitlets-5.0.5 wcwidth-0.2.5 webencodings-0.5.1 widgetsnbextension-3.5.1 WARNING: You are using pip version 21.1.2; however, version 21.1.3 is available. You should consider upgrading via the '/home/carlos/mi_proyecto_dir/mi_proyecto_env/bin/python -m pip install --upgrade pip' command. (mi_proyecto_env)[email protected]:~/mi_proyecto_dir$ jupyter notebook [I 18:20:27.709 NotebookApp] Writing notebook server cookie secret to /home/carlos/.local/share/jupyter/runtime/notebook_cookie_secret [I 18:20:28.151 NotebookApp] Serving notebooks from local directory: /home/carlos/mi_proyecto_dir [I 18:20:28.151 NotebookApp] Jupyter Notebook 6.4.0 is running at: [I 18:20:28.151 NotebookApp] http://localhost:8888/?token=e91cecb366426aa83eee2b176e262267cd70f188147d9d69 [I 18:20:28.151 NotebookApp] or http://127.0.0.1:8888/?token=e91cecb366426aa83eee2b176e262267cd70f188147d9d69 [I 18:20:28.151 NotebookApp] Use Control-C to stop this server and shut down all kernels (twice to skip confirmation). [C 18:20:28.257 NotebookApp] To access the notebook, open this file in a browser: file:///home/carlos/.local/share/jupyter/runtime/nbserver-3327-open.html Or copy and paste one of these URLs: http://localhost:8888/?token=e91cecb366426aa83eee2b176e262267cd70f188147d9d69 or http://127.0.0.1:8888/?token=e91cecb366426aa83eee2b176e262267cd70f188147d9d69
